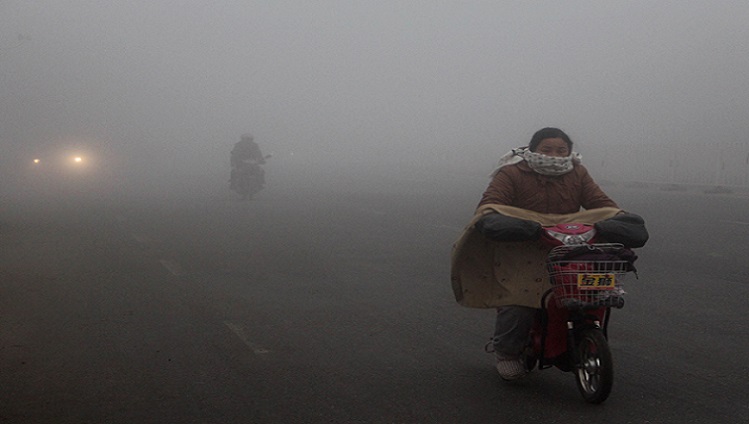

温室効果ガス(GHG)排出量が世界で最も多いのは中国だが、その排出量は実は公表ベースより14%少ないことが、科学雑誌「Nature」に発表された最近の研究論文で明らかになった。
中国では「白髪三千丈」という言葉があるが、研究論文通りだとすると、「CO2排出量も三千丈ならぬ、14%過剰」だったことになる。
Natureに掲載されたのは、hu Liuハーバード大学教授らの共同論文。まず、2010-2012年の間の世界の化石燃料とセメント生産に伴う世界のCO2排出量増加分の4分の3は中国で起きているが、中国の推計には不確実性がかなりある。たとえば2008年の化石燃料からの排出総量の不確実性 は0.3ギガトン分、率にして15%のブレがある、と……
申し訳ありません。 この記事は会員限定です。閲覧権限を与えたユーザーにのみ、記事全文を公開しています。続きをご覧になりたい方は下記フォームよりログインをお願い致します。































 Research Institute for Environmental Finance
Research Institute for Environmental Finance